NOAA - Arctic Tundra Region Now Net Source Of Carbon Dioxide, Not A Sink As It Had Been For Milennia
Mods: Press release.
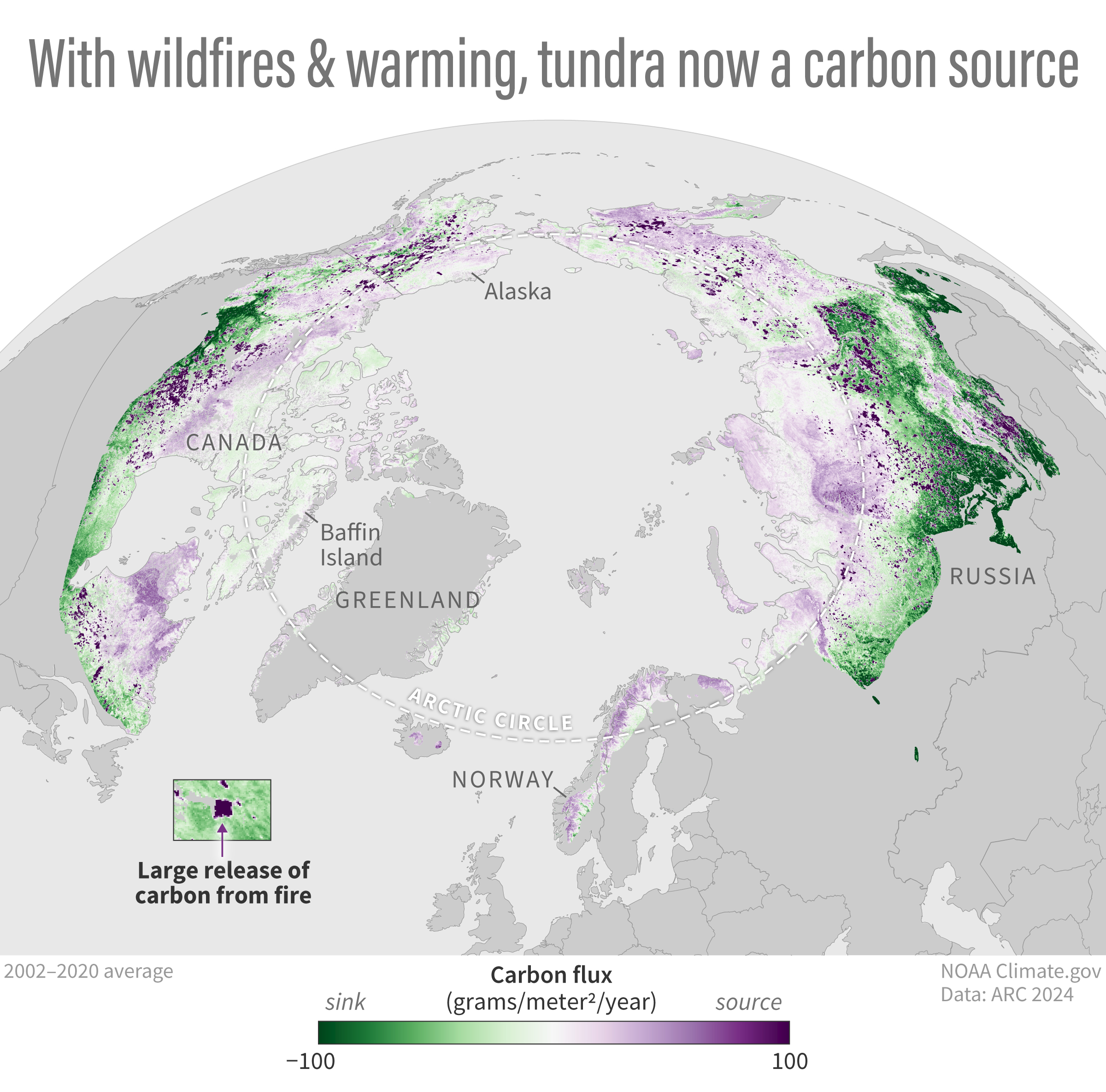
According to NOAA’s Arctic Report Card, the Arctic tundra region has become a source of carbon dioxide and methane to the atmosphere, driven by a combination of microbial activity in thawing permafrost and emissions from wildfires, which are becoming more frequent. In 2024, permafrost temperatures ranked highest on record at nearly half of Alaska’s long-term monitoring stations. Meanwhile, 2024 ranked as the second-highest year for wildfire emissions north of the Arctic Circle.
This map shows the Arctic carbon balance over the past two decades. Land areas that had a net positive carbon dioxide flux, meaning they were a source of carbon to the atmosphere, are colored purple. The darkest purple clusters show areas where there were large releases of carbon dioxide due to wildfires. Green areas had a negative carbon dioxide flux, meaning they were a “sink” that removed and stored atmospheric carbon. From 2001–2020 the Arctic as a whole was carbon neutral, according to the report; however, the tundra region has now shifted from a carbon sink, which it has been for millennia, into a carbon dioxide source, and it remains a methane source. The boreal forest region remains a carbon sink.
“Climate change has been intensifying high-latitude fire regimes, resulting in increased burned area, fire intensity, and carbon emissions. Vegetation regrowth after wildfire often re-sequesters CO2 [carbon dioxide] from the atmosphere over decades following fire, but more frequent and severe fires, combustion of below-ground carbon, and long-term impacts of fire on ground thaw from combustion of vegetation and organic soils are resulting in net carbon emissions to the atmosphere over large spatial scales.”
The land areas of the Arctic have been a carbon sink for thousands of years, meaning there has been a net removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by plants, with long-term storage in the soil and permafrost. However, increasing surface air temperatures are causing permafrost to warm and thaw, allowing stored carbon dioxide and methane to be released into the atmosphere. Wildfires and other disturbances are adding pulse releases of carbon dioxide and methane. These changes together have shifted the Arctic tundra from a net carbon sink into a source.
The 2024 Arctic Report Card includes a detailed report on trends in permafrost temperatures, wildfires, and carbon cycling across the Arctic.
EDIT/END
https://www.climate.gov/news-features/featured-images/2024-arctic-report-card-arctic-tundra-now-net-source-carbon-dioxide
